This post is also available in: Italian
Reading Time: 5 minutesWith the new VMware vSphere 6.0 suite there is also a new version of VMware Virtual SAN (or VSAN) now in version 6.0 (but formally it’s a 2.0 version). Seems still a separated products, althougt my hope is that it may included in some vSphere bundle (like was with the VSA).
This new version brings a lot of new features and now it’s ready also the business critical applications (version 1.0 was more targeded for ROBO, VDI, DR, testing, … scenarios).
The main news about this versions are:
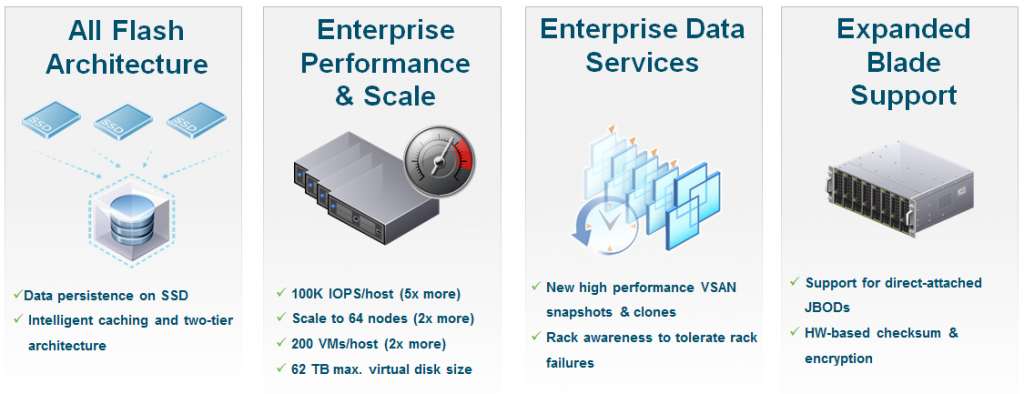
- All Flash Architecture
- Enterprise Performance
- Enterprise Data Services
- Expanded Blade Support
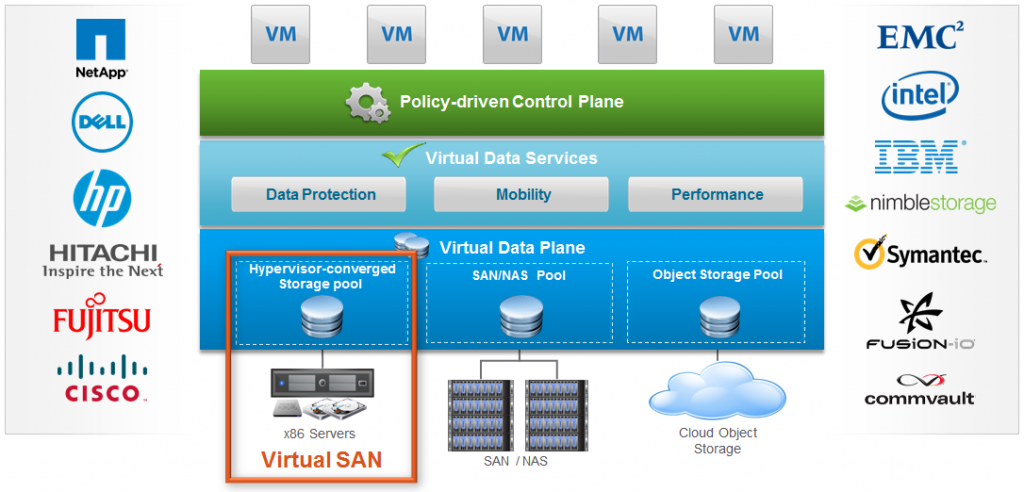
Virtual SAN it’s a radically simple Hypervisor-Converged storage software following the SDS approach of VMware and it’s pretty unique because it’s a software-defined storage built into vSphere (in the core ESXi functions), deeply integrated with the VMware stack and managed through per-VM storage policies.
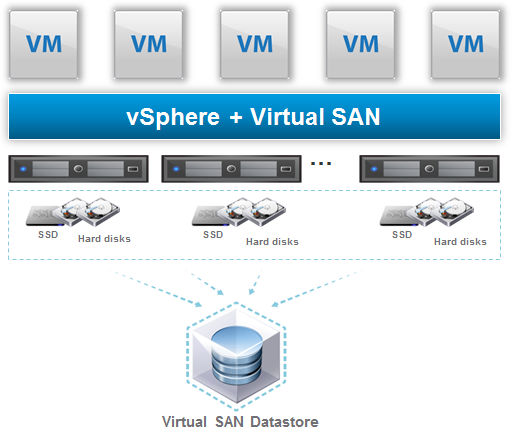
Like other SDS solutions it runs on any standard x86 server and can pool local disk resources (included flash-based devices) into a shared datastore with the same logic of previous version: one VSAN cluster is just a VMware cluster with VSAN enabled (note that you have still to temporally disable vSphere HA before enable VSAN cluster feature). Of course new VSAN limit match the new cluster limit that it’s now 64 hosts.
In the previous picture there was the traditional Hybrid VSAN with a pool composed by Flash and traditions spindle (each host require at least one SSD and one traditional hard disk). In Virtual SAN hybrid ALL read and write operations always go directly to the Flash tier.
Flash based devices serve two purposes in Virtual SAN hybrid architecture:
- Non-volatile Write Buffer (30%)
- Writes are acknowledged when they enter prepare stage on the flash-based devices
- Reduces latency for writes
- Read Cache (70%)
- Cache hits reduces read latency
- Cache miss – retrieve data from the magnetic devices
But starting with Virtual SAN 6.0 there are also the Full Flash VSAN based only on flash, where flash-based devices used for caching as well as persistence:
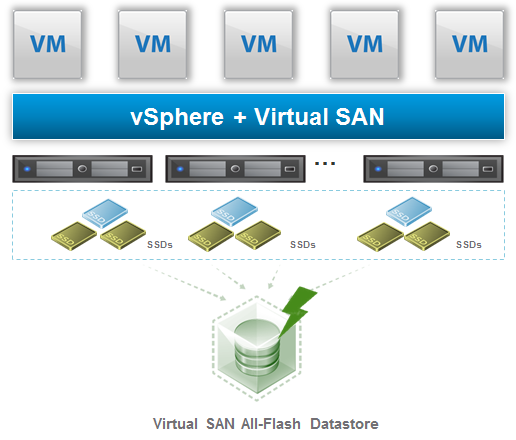 In this case there are still two different tiers (like it happen, for example, in the Dell Compellent full flash solution):
In this case there are still two different tiers (like it happen, for example, in the Dell Compellent full flash solution):
- Cache tier: is 100% write, using write-intensive, higher grade flash-based devices (usually SLC)
- Capacity tier: that it’s the persistent storage and can leverage lower cost read-intensive flash-based devices (usually MLC)
The main advantage of a full flash solution is to have consistent performance with sub-millisecond latencies (although good hybrid solutions with QoS or similar services can provide predictable performance), but of course there are also some specific user cases (mainly where a mechanical part is not accepted, like for environmental reasons).
Network requirement are still the same of VSAN 1.0, but note that now layer 3 network configuration is supported in 6.0.
For the performance and scale improvements, the new cluster size is not the only changes:
- 2x VMs per host: in order to have larger consolidation ratios
- 62TB Virtual Disks are now supported also on VSAN
- up to 32 snapshots per VMs
- new on-disk format (instead of the previous VMFS-L format)
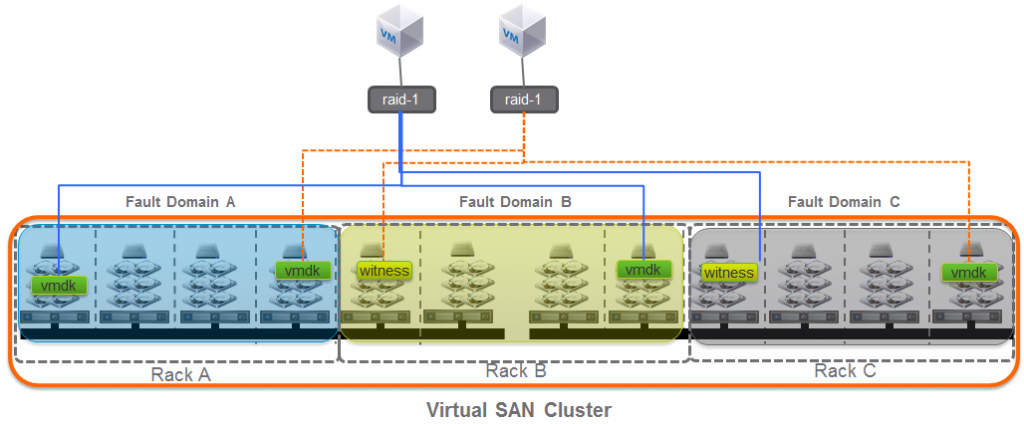
For the availability aspects, the new VSAN introduce a new important concept of fault domain in order to provide the ability to group multiple hosts within a cluster according with possible fault scenarios. Virtual SAN Fault Domains ensures replicas of VM data is spread across the defined failure domains. Fault domains provide the ability to tolerate:
- Rack failures
- Storage controller
- Network failures
- Power failure
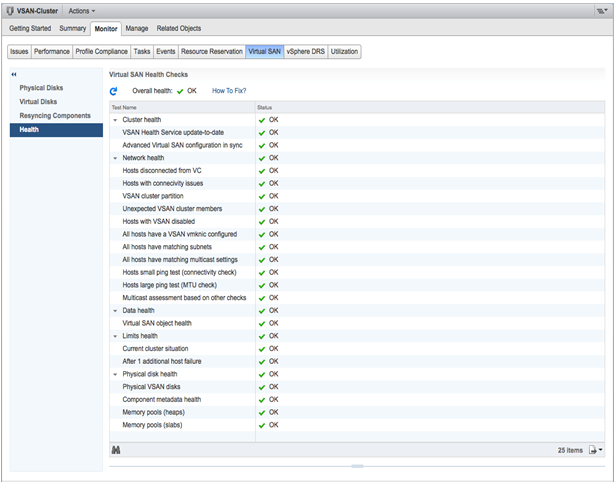
Also the healt of a VSAN based solution could now be monitor in a easiest and simple way though the new Virtual SAN Health Service, designed to deliver troubleshooting and health reports to vSphere Administrators about Virtual SAN 6.0 subsystems and their dependencies such as Cluster Health, Network Health, Data Health, Limits Health, Physical Disk Health.
About the blade support is mainly a compatibility aspect: blades usually does not have enought local space for disks, but there can be JBOD solution to provide DAS storage to each blade… so basically it’s just an increades HCL for VSAN were direct attached and disks (flash devices, and magnetic devices) are supported with combination of direct attached disks and high density attached disks (SSDs and HDDs) per disk group.
About HCL, please remember that VSAN HCL is different compared with tradition vSphere HCL, just because the right controller and flashes are a key differentiator for this kind of environments.
You can choose to build your own VSAN following the right HCL, or you can simple buy VSAN ready node from common hardware vendors. Or you can have an entire Hyper-Converged Infrastructure with EVO:RAIL.
For fome information see also: